
How to Choose CNC Machining Parts: Key Specifications & Material Tips
Date:2026-01-27Article editor:Starting Point PrecisionViews:40Choosing the right CNC machined parts is critical for the success of your project, affecting performance, cost, and lead time. This guide breaks down the key specifications and material selection tips to inform your decision-making process.
Understanding Key Specifications
Several technical specifications directly influence the manufacturability and function of your part.
1. Dimensional Tolerances
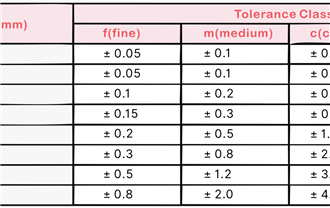
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in a part's dimensions. Standard tolerances are typically sufficient for many applications, but tighter tolerances increase cost and time. Always specify the tightest tolerance necessary for your part's function—and no tighter. For a deep dive, read our guide on Understanding CNC Tolerances .
2. Geometric Complexity
CNC machining excels at creating complex geometries, but certain features are more challenging. Deep pockets, internal sharp corners, extremely thin walls, and non-standard thread types can raise costs. Design for manufacturability (DFM) principles is key. Consider using Autodesk Fusion 360 for DFM analysis.
3. Surface Finish Requirements
The desired surface finish impacts the machining process and cost. A standard milled finish (Ra 3.2 μm) is often adequate. If a smoother finish is needed for aesthetics or function (e.g., sealing), secondary operations like polishing or bead blasting will be required.
4. Production Volume & Lead Time
CNC machining is ideal for low to medium volume production. For very high volumes, injection molding might be more economical. Clearly communicate your required lead time, as it affects machine scheduling and pricing.
Selecting the Right Material
Material choice is paramount, dictating the part's strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost.
1. Metals
Aluminum (e.g., 6061. 7075): The most common choice. Offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good machinability, and corrosion resistance. Ideal for aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics parts.
Stainless Steel (e.g., 304. 316): Chosen for its superior strength, durability, and excellent corrosion resistance. Used in medical devices, food processing, and marine applications.
Titanium (e.g., Grade 5): Extremely strong, lightweight, and biocompatible, but more expensive and difficult to machine. Essential for aerospace and medical implants.
2. Plastics
ABS: A tough, impact-resistant plastic, good for prototypes and functional parts.
POM (Delrin): Known for its high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. Perfect for gears, bearings, and insulators.
PEEK: A high-performance engineering plastic with exceptional thermal and chemical resistance. Used in demanding automotive, aerospace, and medical fields. For more on advanced plastics, visit Material Properties Database .
3. Key Selection Criteria
Mechanical Properties: Consider the required tensile strength, hardness, and impact resistance.
Environmental Factors: Will the part face moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures?
Post-Processing: Do you need plating, anodizing (for metals), or painting? Ensure your base material is compatible.
Conclusion
Successful CNC part selection hinges on balancing your design specifications with practical manufacturing considerations. Start by defining the critical functional tolerances and geometric needs of your part. Then, choose a material that meets your performance requirements while remaining cost-effective to machine. Always consult with your manufacturing partner early in the design phase. Their expertise can help optimize your design for cost, speed, and reliability.

Copyright © 2019 All Rights Reserved Dongguan Starting Point Precision Technology Co., Ltd. Tel: +86-769-82855591
Add: No. 332 Zhen'an Middle Road, Chang'an Town, Dongguan, Guangdong, China